Are you ready for a colorful journey into the powerful world of ACES? Read the article and learn everything you need to understand and adopt this accurate and professional workflow!
Introduction to Color Space.
Establish a solid color-space foundation before embarking on ACES (Academy Color Encoding System). This section will take you through the concept of color space, which acts as a common language for all your color needs, from capture to display. We'll explore how different color spaces define the vast spectrum of colors we perceive and how these spaces impact the way we see and work with images. This article on understanding color representation is a crucial step toward controlling the full potential of ACES. So, let's start unpacking the secrets of color space!
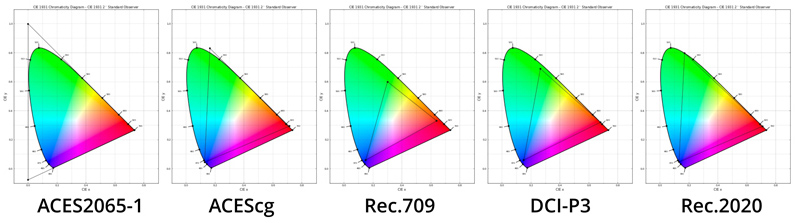 Image by the Autodesk Help Guide. It shows examples of color gamut, which is the range of colors (the triangles) within the color space. ACES2065-1 even exceeds the color coverage of the human eye. ACEScg for example, covers a large range of color space and is used mainly in CG and VFX.
Image by the Autodesk Help Guide. It shows examples of color gamut, which is the range of colors (the triangles) within the color space. ACES2065-1 even exceeds the color coverage of the human eye. ACEScg for example, covers a large range of color space and is used mainly in CG and VFX.
Definition of Color Space.
A color space is a map, a crafted system for describing and encoding the vast spectrum of colors our eyes can perceive. Imagine it as a giant 3D container where each point represents a specific color with defined brightness and position. Different color spaces, like sRGB and Adobe RGB, have varying capacities within this container, encompassing a broader or narrower range of colors.
Understanding color space is crucial—it dictates how faithfully colors are captured, stored, and displayed across devices like cameras, monitors, and printers. Understanding this idea will help you become much better at using ACES, allowing you to achieve incredibly accurate colors in your work.
The definition of Color Space is very well explained with quite simple examples by Cullen Kelly in this video below:
Why Color Space Matters: The foundation of accurate color.
Let's think about a vibrant sunset that appears washed out on your screen or a photorealistic image in print that looks blurred and lifeless. This is the reality without a well-defined color space.
A color space is a universal language that defines the gamut, or the range of colors, a device can capture, display, or output. Just like using the same measuring system ensures everyone understands the length of a meter, a consistent color space allows everyone involved in the creative process to see and manipulate colors similarly.
This is crucial for tasks like 3d art, photography editing, graphic design, and filmmaking, where color plays a vital role in conveying emotions, information, and aesthetics.
The video below is from a meeting in Hollywood discussing how to make movies look good in both HDR and SDR formats. HDR is a newer format that shows more detail, but there are no clear rules yet on creating content for it. Experts will give talks and answer questions such as:
- What does it mean for HDR and SDR versions to “match”? Should they?
- Which deliverable comes first?
- What’s the best way to manage LUTs and looks?
- Can ACES be a creative and technical facilitator for HDR/SDR workflows?
Transforms are being considered for the ACES 2.0 release.
General Advantages of Using ACES Color Space.
The advantages of using ACES color space are its noticeable creativity and flexibility. It's a revolution in color management, unlocking several advantages for all related professionals and color lovers.
Advantage 1: Superior Color Management.
ACES excels in color management by offering several key benefits, such as more prosperous and vibrant colors, consistent color throughout the workflow, greater creative flexibility, and future-proof archiving.
Advantage 2: High Dynamic Range.
ACES is strong at handling HDR imagery as it captures the vast range of light and shadow details in real-world scenes. A standard color space might struggle to represent the blazing highlights and the subtle details in the shadows, leading to clipped whites or crushed blacks. ACES solves this problem by offering more lifelike pictures, with details in bright and dark areas, just like in real life.
Here's a breakdown of how ACES benefits HDR:
Preserved Details: It prevents detail loss, ensuring the preservation of all the information captured by the camera.
Increased Realism: The broader range of brightness values translates to a more lifelike image, replicating how we perceive the world.
Greater Flexibility in Post-Production: ACES provides a robust foundation for color grading, allowing for more creative control over highlights, shadows, and overall contrast in your HDR content.
Advantage 3: Better Workflow Integration.
Making everything in your project look the same throughout is easier if you use a system that works the same way at every step. ACES is like a common language that lets everyone working on the project (like video editors and special effects artists) understand each other better. This makes it faster and easier to get things done.
Here's how ACES gives a better-integrated workflow:
Universal File Format: It utilizes a standard file format, facilitating effortless footage exchange between different applications, such as cameras, editing suites, VFX software, and color grading tools. This eliminates the need for time-consuming conversions and potential quality loss during transfer.
Simplified Color Management: It removes the guesswork from color management. Working in a scene-referred color space allows you to focus on creative decisions rather than technical adjustments. Colors are accurately represented throughout the pipeline, ensuring consistency and reducing the need for extensive color correction in each software.
Enhanced Collaboration: It fosters better collaboration between various project teams. Everyone works with the same color information, spending less time resolving color discrepancies.
Future-Proof Archiving: Its files are built to last. The open-source nature ensures long-term accessibility and readability of your project's color data, even as software and technology evolve.
Advantage 4: Preservation of Image Data.
ACES is also helpful in preserving the richness of image data throughout the post-production workflow because, as we already mentioned above, it can handle a wider color gamut and high dynamic range information. The captured colors, with all their subtleties and nuances, are maintained more faithfully throughout editing, grading, and final delivery.
Advantage 5: Uniformity and Consistency.
ACES shines in its ability to maintain consistent color throughout your entire workflow, from acquisition to editing and final distribution. It provides a unifying language for color which translates to several key benefits:
Predictable Results: ACES makes colors predictable, like magic! There are no more surprises when you see them on different screens or at the end. This saves you time fixing colors and makes your workflow smoother.
Simplified Collaboration: People working in different places can easily use the same colors, even using different computers. This way, the colors always look the same, saving people time from fixing them.
Future-Proof Archiving: ACES is an open-source, non-proprietary system, meaning it's not tied to specific cameras or software. This ensures your color data remains accessible and interpretable even as technology evolves, safeguarding the future value of your content.
Difference between ACES and Other Color Spaces.
While color spaces like sRGB are workhorses for everyday displays, ACES offers a new level of color control, which is why it is preferred by professionals seeking the best possible color experience. It boasts a much wider color gamut and a High Dynamic Range (HDR), crucial for replicating real-world scenes with bright skies and dark corners.
The technology keeps evolving, with displays capable of showcasing ever-wider gamuts. ACES is designed to adapt to these advancements, making your content future-proof as display capabilities improve.
In the video below, "Color Space vs. Color Gamut" you can find a nice explanation through Real-World examples:
Comparison of ACES and sRGB.
The critical differences between ACES and sRGB are:
Gamut: ACES boasts a significantly wider color gamut, encompassing a more extensive range of colors visible to the human eye. In contrast, sRGB, designed for monitors, has a more limited range. This wider gamut in ACES allows for more lifelike and nuanced colors, especially in highlights and shadows.
Dynamic Range: ACES offers high dynamic range (HDR) capabilities, which can handle a broader spectrum of light and dark values. This translates to a more realistic representation of scenes with both bright and dark elements. Conversely, sRGB has a standard dynamic range, which can lead to clipping, which means a loss of detail in highlights and shadows.
Workflow Flexibility: ACES is a scene-referred color space that preserves color information throughout the production pipeline, from capture to final output. This allows for greater flexibility in color grading and effects application without sacrificing color accuracy. sRGB, being a display-referred space, is designed for final presentation and may require color adjustments during the workflow to maintain consistency.
Target Audience: ACES is primarily used in professional film, television, and high-end VFX workflows where color accuracy and creative control are essential. sRGB, on the other hand, is the standard color space for most computer monitors, web browsers, and everyday digital content.
In essence, ACES provides a future-proof color pipeline with exceptional color fidelity and flexibility. Meanwhile, sRGB remains the go-to for web and standard displays.
Below is a pretty informative video with 3D-related content in Maya.
Case Studies: Effectiveness of ACES in Different Fields.
In this section, we explore ACES's real-world applications, showcase its effectiveness in various fields, and discuss how ACES has revolutionized workflows, streamlined collaboration, and delivered superior results.
ACES in Film Production and Television.
It fosters consistent color across filming, editing, and visual effects, ensuring a seamless pipeline and stunning visuals on screen.
ACES in Animation and VFX.
It empowers studios to create vibrant and consistent colors within complex 3D environments, leading to more efficient workflows and photorealistic rendering.
ACES in Game Development.
It enables game developers to achieve unmatched color fidelity across diverse platforms, delivering a visually immersive gaming experience.
ACES in Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality.
It facilitates the creation of realistic and color-accurate VR and AR experiences, enhancing user engagement and blurring the lines between reality and simulation.
ACES in Photography.
While ACES revolutionizes color workflows in film and high-end video production, its role in digital photography remains debated.
Currently, dedicated photo editing software with robust ACES integration is limited. This means working with it in photography often requires using workarounds or plugins, potentially slowing down your workflow
ACES utilizes a scene-referred workflow. Extracting the most out of it often requires a good understanding of color grading principles, adding a learning curve for photographers. Finally, it won't magically improve a poorly exposed or composed image. For most everyday photographers, the advantages of ACES might not outweigh the current limitations.
However, if you're a professional photographer working on high-end projects or want to future-proof your workflow and have the technical expertise, ACES offers a path to exceptional color fidelity and flexibility.
ACES in Graphic Design.
ACES eliminates the frustration of color shifts when moving from design software to print or digital displays with different color profiles. It helps to maintain consistent brand colors across print and digital platforms by providing a reliable color foundation.
Accurate color representation is paramount in packaging design. It helps designers create packaging that faithfully reflects the intended colors, making the product appealing and consistent on store shelves.
For designers creating mockups for presentations or client approvals, it ensures the colors displayed accurately represent the final output.
How to Implement ACES Color Space in Your Workflow.
You'll definitely need a robust toolkit to leverage ACES's magic and full potential. Keep in mind that the list below is not exhaustive. New tools and software are constantly emerging to support ACES workflows. The key is identifying solutions that seamlessly integrate with your existing pipeline.
Necessary Tools and Software.
Different tools support ACES. For example, color correction software like DaVinci Resolve allows editing directly in ACES for maximum control. Color management tools convert colors between cameras and ACES. Some cameras and editing software now also work with it directly. Last but not least, there are viewing applications like the ACES Reference Display that show footage accurately on calibrated screens.
| DaVinci Resolve | Blackmagic Design Fusion | Foundry Nuke |
| FilmLight Baselight | Adobe Premiere Pro | Adobe After Effects |
| OpenColorIO | Autodesk Maya | Autodesk 3DS Max |
| Unreal Engine | Mocha Pro | Avid Media Composer |
| Final Cut Pro |
Step-by-step Guide to Switching to ACES.
Switching to ACES color space involves configuring your software to handle this workflow. Here's a general overview of the steps involved:
Software Support: Ensure your editing software supports ACES. Most professional editing applications offer compatibility.
Project Settings: Locate the project settings within your software. Look for a color management section where you can specify the working color space.
Select ACEScg: Choose ACEScg (ACES Common Gamut) as your working color space. This is the recommended space for most editing tasks within the ACES workflow.
Input Color Space: Define how your source files (images/videos) will be interpreted. You might need to establish a preset for different input types (e.g., Rec.709 for standard footage).
Output Color Space: Decide the output color space depending on your final destination (e.g., Rec.709 for web delivery, DCI-P3 for digital cinema).
OCIO Configuration: Some software might require selecting an OCIO configuration file. This file contains specific instructions for handling ACES within your chosen application.
Viewer LUT: You can set a viewer LUT (Look Up Table) to simulate how your final output will look on a standard display, as ACEScg is a linear space not optimized for direct viewing.
Learn what is Rec.709 in the video below:
Conclusion.
In conclusion, this guide has explored the complexities of color space and how ACES offers a future-proof solution for consistent and efficient color management. By adopting it, you can ensure the fidelity of your work across different stages of production and viewing environments. Take the next step and explore the resources available from the official ACES Central website to unlock its full potential in your projects.
Thank you for reading this article. We hope that you now have a clearer understanding of Color Space and ACES and how you can benefit from it!
Kind regards & keep rendering! 🧡

About the author
Vasilis Koutlis, the founder of VWArtclub, was born in Athens in 1979. After studying furniture design and decoration, he started dedicating himself to 3D art in 2002. In 2012, the idea of VWArtclub was born: an active 3D community that has grown over the last 12 years into one of the largest online 3D communities worldwide, with over 160 thousand members. He acquired partners worldwide, and various collaborators trusted him with their ideas as he rewarded them with his consistent state-of-the-art services. Not a moment goes by without him thinking of a beautiful image; thus, he is never concerned with time but only with the design's quality.
